Michael Merzenich the father of brain plasticity science. Neuroscientists tried to argue the opposite.
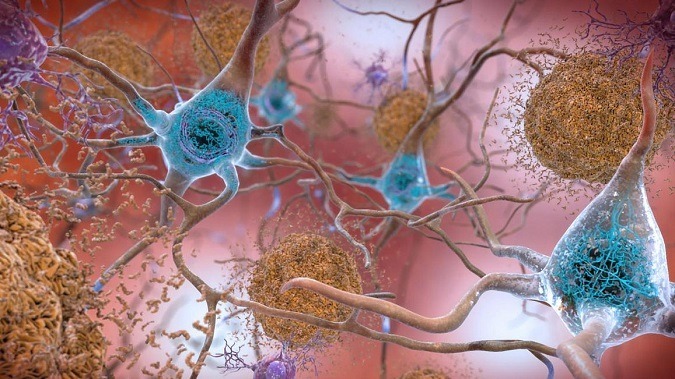
Brain Plasticity How Learning Changes Your Brain Sharpbrains
As we experience an event or learn a new skill new connections are formed between neurons and connections that arent needed anymore are eliminated.

. Brain plasticity is a relatively recent concept to come from neuropsychology that describes the brains inherent ability to rewire itself out of necessity. Neuroplasticity or brain plasticity is the ability of the brain to modify its connections or re-wire itself. Neural connections can be forged and refined or weakened and severed.
Brain plasticity theory is the exploration of the changes that occur in the brain. Previously neuroscientists believed that the structure and functions of the brain molded until adulthood. With every new experience the brain changes in some way.
Neuroplasticity can explain a broad range of facts about the structure and function of the brain. Brain plasticity is an intrinsic property of the nervous system that allows an individual to adapt to a rapidly changing environment through strengthening weakening pruning or adding of synaptic connections and by promoting neurogenesis Feldman 2009. When the patients were asked to describe.
Ability to learn or acquire new skills. Zoom meeting tips and tricks with Prezi Video. It can change develop and rearrange.
These involve the gradual decline of neuroplasticity w. Thats where brain plasticity also called neuroplasticity or Neuronal plasticity and the science of plasticity psychology comes in. Split-brain or callosal syndrome is a type of disconnection syndrome when the corpus callosum connecting the two hemispheres of the brain is severed to some degree.
Pascual-Leone et al 2005. This notion does however have some constraints. Brain plasticity is the brains ability to adapt to change across the lifespan and to rewire itself after damage.
Brain plasticity is the inherent ability of the brain to adapt or modify its connections or synapses. The recovery from brain injuries such as Trauma and stroke. Thats what plasticity means.
Gray matter can actually shrink or thicken. While it is evident that the brain changes with age and even deteriorates to some degree it is also important to remember that environment can have an impact on the brain. The geographic layout of the brain isnt set in stone.
Brain plasticity also called neuroplasticityis an odd term for most people with the word plastic causing images of Tupperware or Saran Wrap to pop into your head. The large outer layer of the brain known as the cortex is especially able to make such modifications. How to brand your meeting with Prezi Video.
In other words it is the ability of the brain to rewire itself. How to make a. According to Carr people have used the term use it or lose it to aptly describe the best way to off.
This theory is also referred to as neuroplasticity. It is an association of symptoms produced by disruption of or interference with the connection between the hemispheres of the brain. As humans grow and develop their brains are constantly being altered as they consume new information.
Brain plasticity is vital in the. There are six concepts that are important to understand brain plasticity. Plasticity or neuroplasticity describes how experiences reorganize neural pathways in the brain.
Where previously the brain was thought to be static after a certain age and damage permanent psychologists now believe that the brain is constantly regrowing repairing itself and rewiring. A protein member of the neurotrophin family that supports the survival of existing neurons and that encourages the growth and differentiation. Then people could lose brain cells or that the structure of their mind was set in place.
Development of humans from infancy to adulthood. Brain plasticity science is the study of how brain change happens and the outcomes that take place as a result of this change. Without this ability any brain.
Want to achieve your Peak Performance. Accordingly plasticity should be defined as a balance between the cell-intrinsic potential for structural changes depending on neuronal maturation and the limits or opportunities provided by the surrounding environment depending on brain maturation. These changes in neural connections are what we call neuroplasticity.
Brain plasticity also called neuroplasticity refers to the brains ability to change throughout life Michelon 2008. For example plasticity explains how you learn to sing a new song just by hearing it on your car radio. Long lasting functional changes in the brain occur when we learn new things or memorize new information.
However brain plasticity is a common term used by neuroscientists referring to the brains ability to change at any agefor better or worse. Then in the 1940s and 1950s came the second force behaviourism courtesy of people like Skinner and Watson. The term brain plasticity also known as neuroplasticity is related to our nervous systems ability to modify itself both functionally and structurally.
In a literal sense plasticity is a physical objects ability to be physically manipulated. This happens naturally as time goes on but also in response to injuries. Brain Plasticity and Trauma Fourth Force in Psychology The first force in psychology was psychoanalysis brought to us by Sigmund Freud.
The ability of the brain to durably change its structure. Brain plasticity also known as neuroplasticity is the process in which your brain changes its wiring. Brain plasticity from the Greek word plastos meaning molded refers to the extraordinary ability of the brain to modify its own structure and function following changes within the body or in the external environment.
Later in the 1960s Rogers and Maslow introduced humanism the third force in psychology. Plasticity is a term that describes the brains ability to change both its structure and function in response to the world around it. Neurogenesis Synaptogenesis Synaptic pruning Long term potentiation LTP Long term depression LTD Myelin plasticity or myelination.
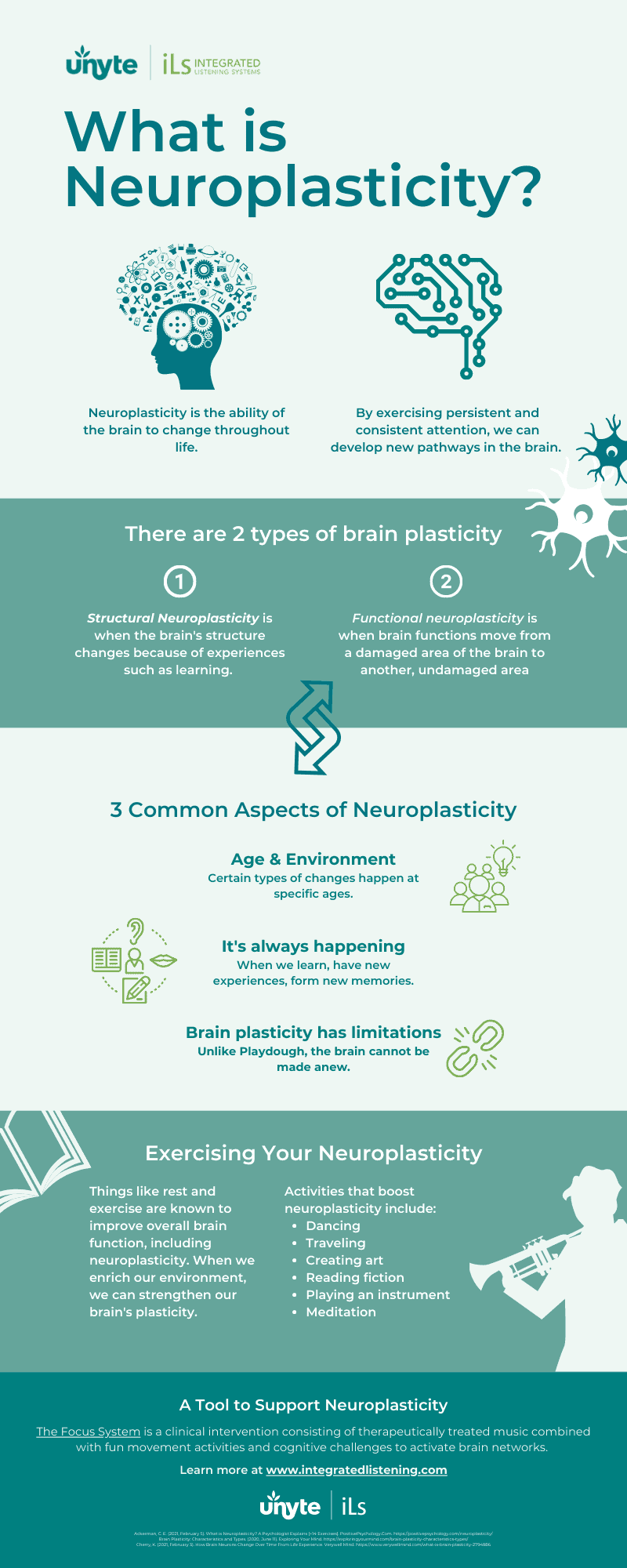
Infographic A Beginners Guide To Neuroplasticity Unyte Integrated Listening

Major Mechanisms Involved In Brain Plasticity The Diagram Explains The Download Scientific Diagram

Neuroplasticity How Your Life Shapes Your Brain The Best Brain Possible Neuroplasticity Brain Facts Best Brains

Mind And Brain Plasticity Processes During Acute State And Follow Up Download Scientific Diagram
0 Comments